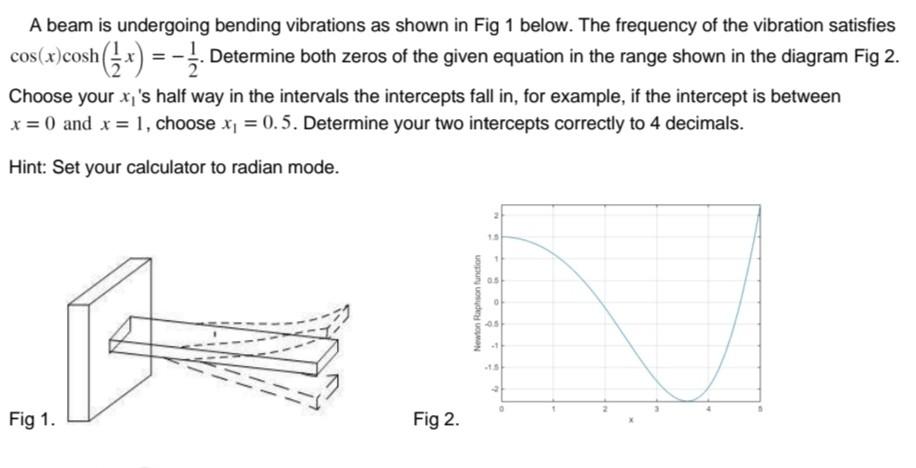
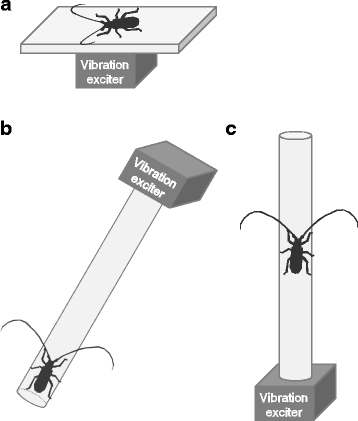
Substrate vibrations mediate behavioral responses via femoral
4.6 (337) · $ 11.00 · In stock
Background Vibrational senses are vital for plant-dwelling animals because vibrations transmitted through plants allow them to detect approaching predators or conspecifics. Little is known, however, about how coleopteran insects detect vibrations. Results We investigated vibrational responses of the Japanese pine sawyer beetle, Monochamus alternatus, and its putative sense organs. This beetle showed startle responses, stridulation, freezing, and walking in response to vibrations below 1 kHz, indicating that they are able to detect low-frequency vibrations. For the first time in a coleopteran species, we have identified the sense organ involved in the freezing behavior. The femoral chordotonal organ (FCO), located in the mid-femur, contained 60–70 sensory neurons and was distally attached to the proximal tibia via a cuticular apodeme. Beetles with operated FCOs did not freeze in response to low-frequency vibrations during walking, whereas intact beetles did. These results indicate that the FCO is responsible for detecting low-frequency vibrations and mediating the behavioral responses. We discuss the behavioral significance of vibrational responses and physiological functions of FCOs in M. alternatus. Conclusions Our findings revealed that substrate vibrations mediate behavioral responses via femoral chordotonal organs in M. alternatus.

PDF) Substrate vibrations mediate behavioral responses via femoral
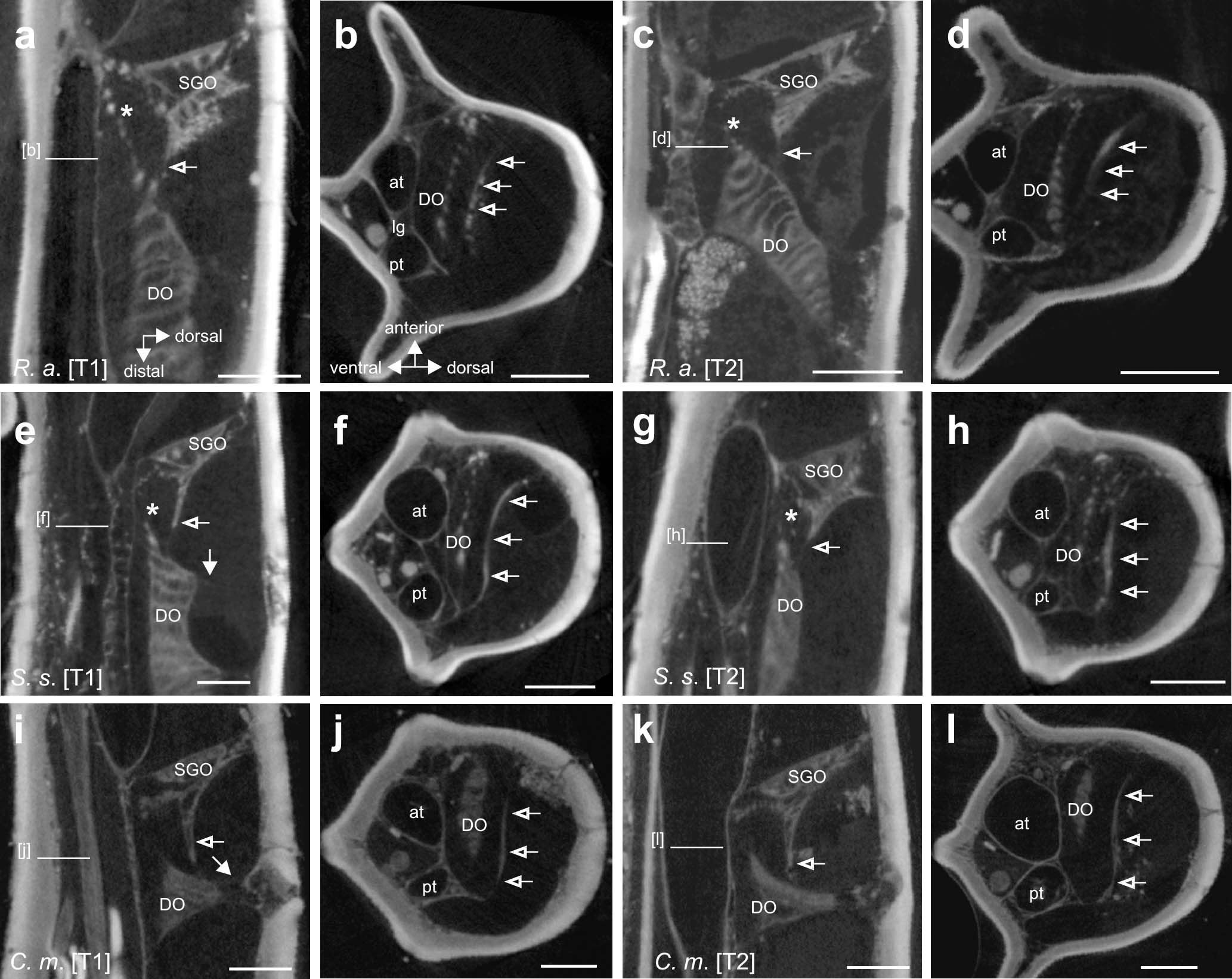
Frontiers The Subgenual Organ Complex in Stick Insects

Functional architecture of neural circuits for leg proprioception in Drosophila - ScienceDirect

Communication by substrate-borne mechanical waves in insects: From basic to applied biotremology - ScienceDirect
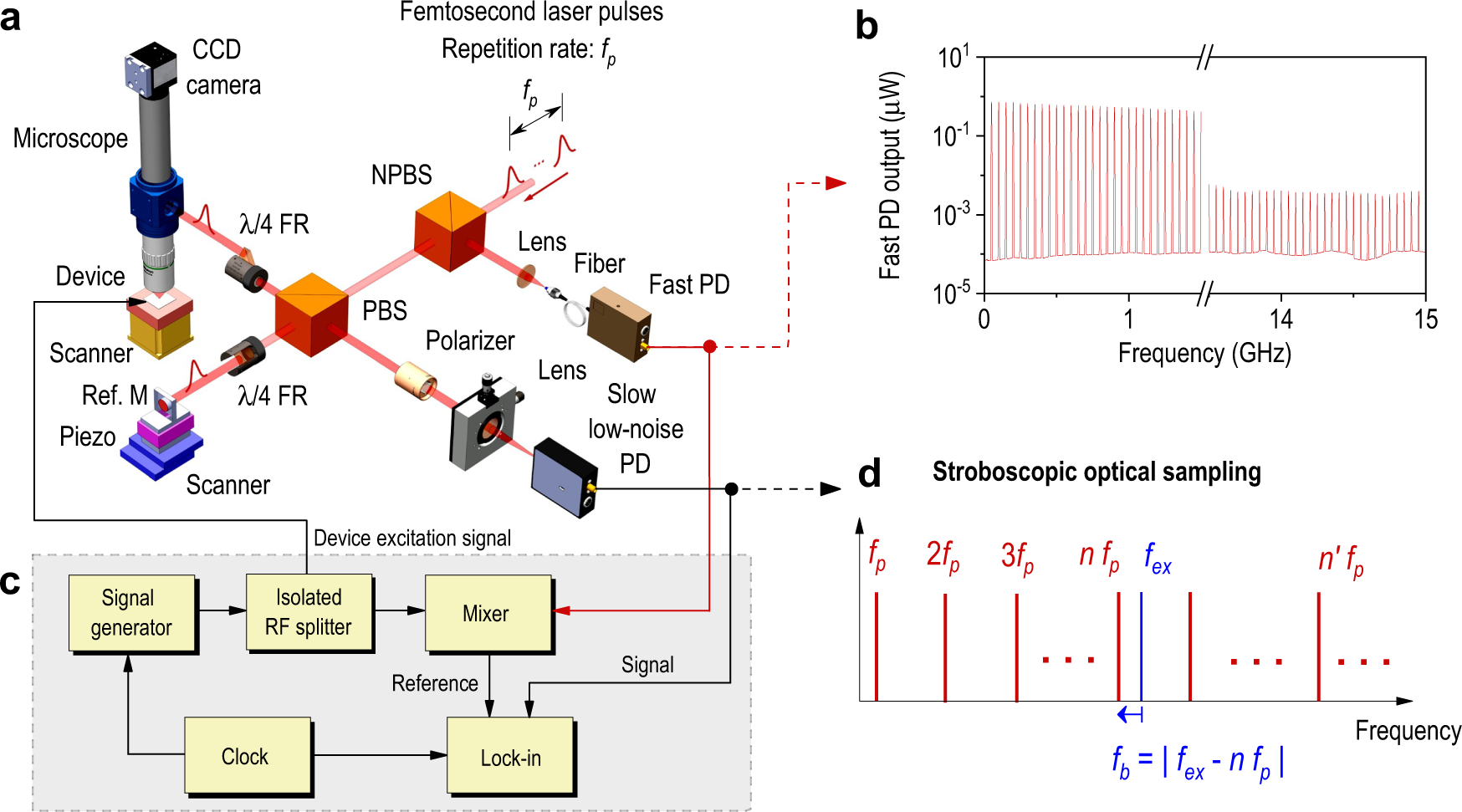
Femtometer-amplitude imaging of coherent super high frequency vibrations in micromechanical resonators

Central processing of leg proprioception in Drosophila
Frontiers How Swift Is Cry-Mediated Magnetoreception
Cell-mediated substrate deformation. (a, b) The representative displacement

Emergence of a somatosensory tonotopic map for substrate vibration in the brainstem

PDF) Physiology of vibration-sensitive afferents in the femoral

Mean phase propagation velocity of simulated bending waves, measured
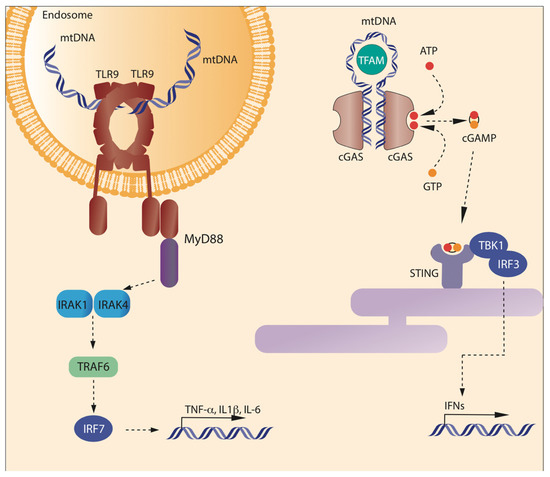
Cells, Free Full-Text

Drosophila females receive male substrate-borne signals through specific leg neurons during courtship - ScienceDirect
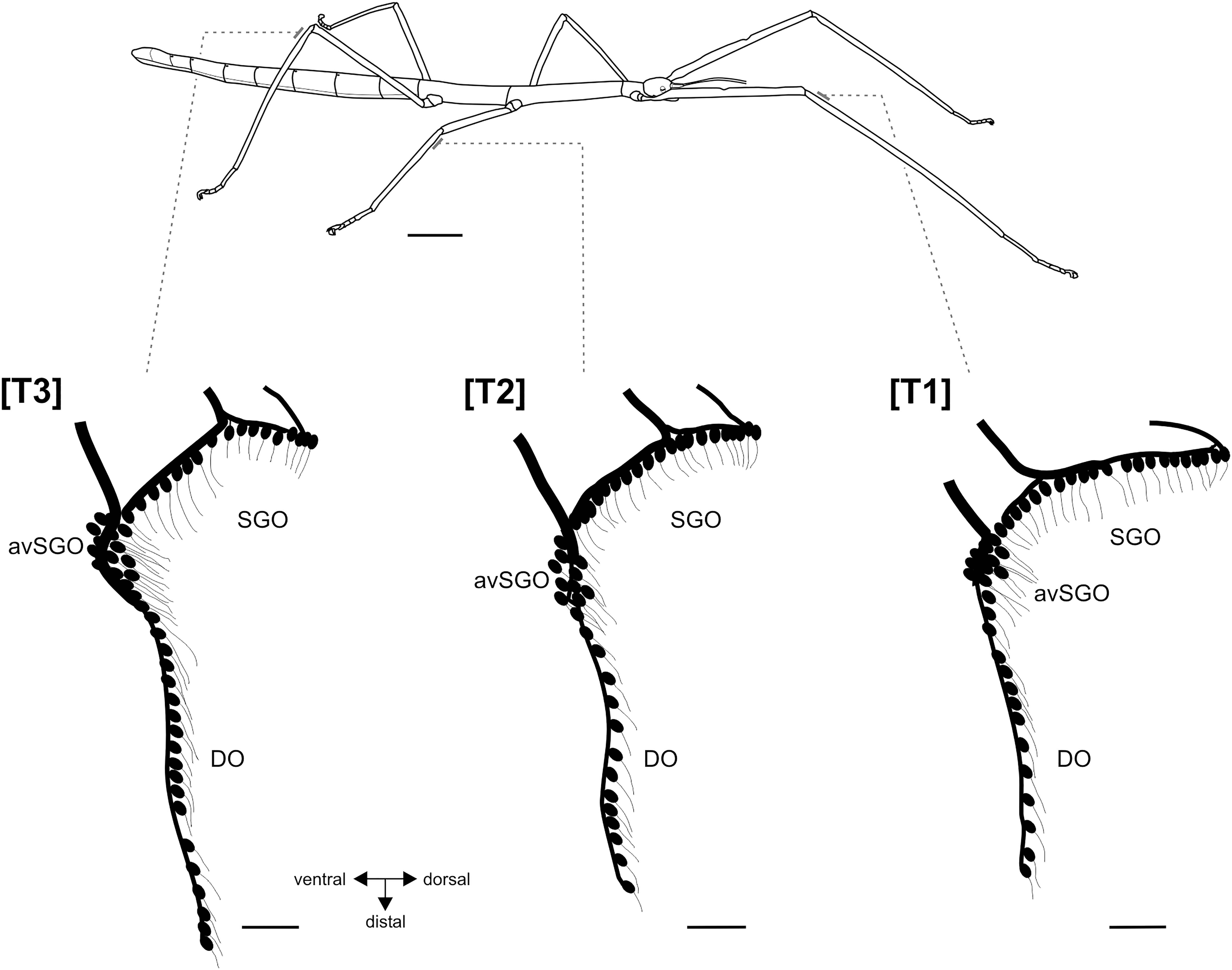
Frontiers The Subgenual Organ Complex in Stick Insects