- Home
- compression factor equation
- The compression factor (compressibility factor) for 1 mol of a van der
The compression factor (compressibility factor) for 1 mol of a van der
4.7 (197) · $ 5.99 · In stock
For 1 mol of a gas, the van der Waals equation is (P+(a)/(V(m)^(2)))(V(m)-b)=RT Ignoring b, we get (given volume of gas molecule is negligible) (P+(a)/(V(m)^(2)))V(m)=RT ltbgt or pV(m)+(a)/(V(m))=RT or (pV(m))/(RT)+(a)/(V(m)RT)=1 or Z=(pV(m))/(RT)=1-(a)/(V(m)RT) (i) It is given that Z=(pV(m))/(RT)=0.5implies V(m)=(0.5RT)/(P) With this, equation (i) becomes 0.5=1-(a)/((0.5RT//p)RT) or a=(0.5)((0.5RT)/(p))RT=0.25(R^(2)T^(2))/(p) Substiuting the given values, we get a=(0.25)[((0.082L atm K^(-1)mol^(-1))^(2)(273 K)^(2))/((100 atm))] =1.2528 L^(2) atm mol^(-2)

Malayalam] The Compressibility factor for one mole of a van der Waal

A 672 ml of a mixture of oxygen - ozone at N.T.P. were found to be wei

The final product Z in the following reaction is

A 2.0 L container at 25^(@)C contain 1.25 mol of O(2) and 3.2 mol of C
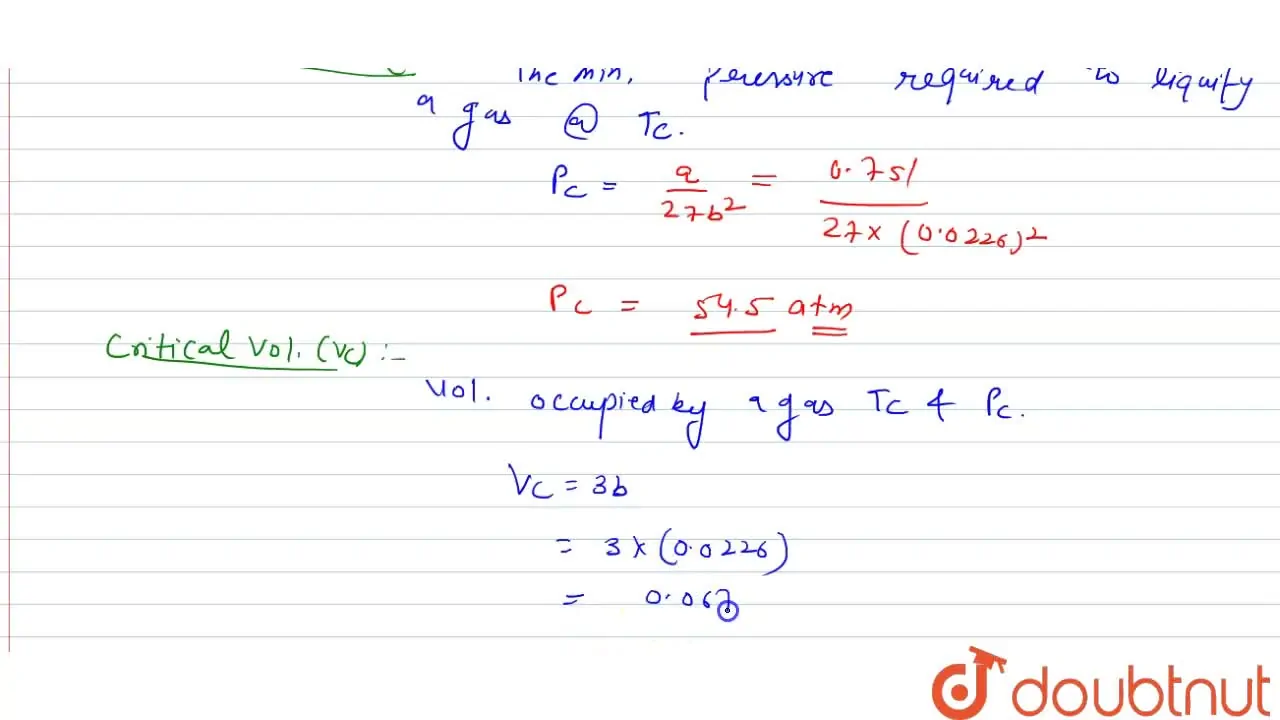
Calculate the critical constants of a gas whose van der Waals constant

A mixture of ideal gases is cooled up to liquid helium temperature 4.2

The density of the vapour of a substance at 1 atm pressure and 500 K i
The compression factor (compressibility factor) for one mole of a

is characterised by van der Waals coefficients that are dependent on t