Medicina, Free Full-Text
4.8 (477) · $ 16.50 · In stock
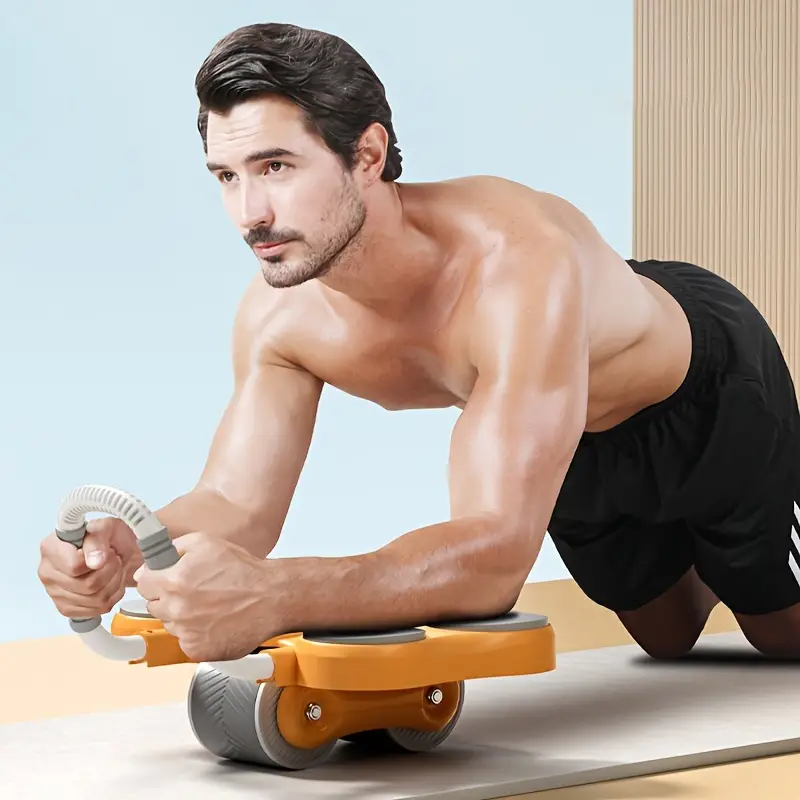
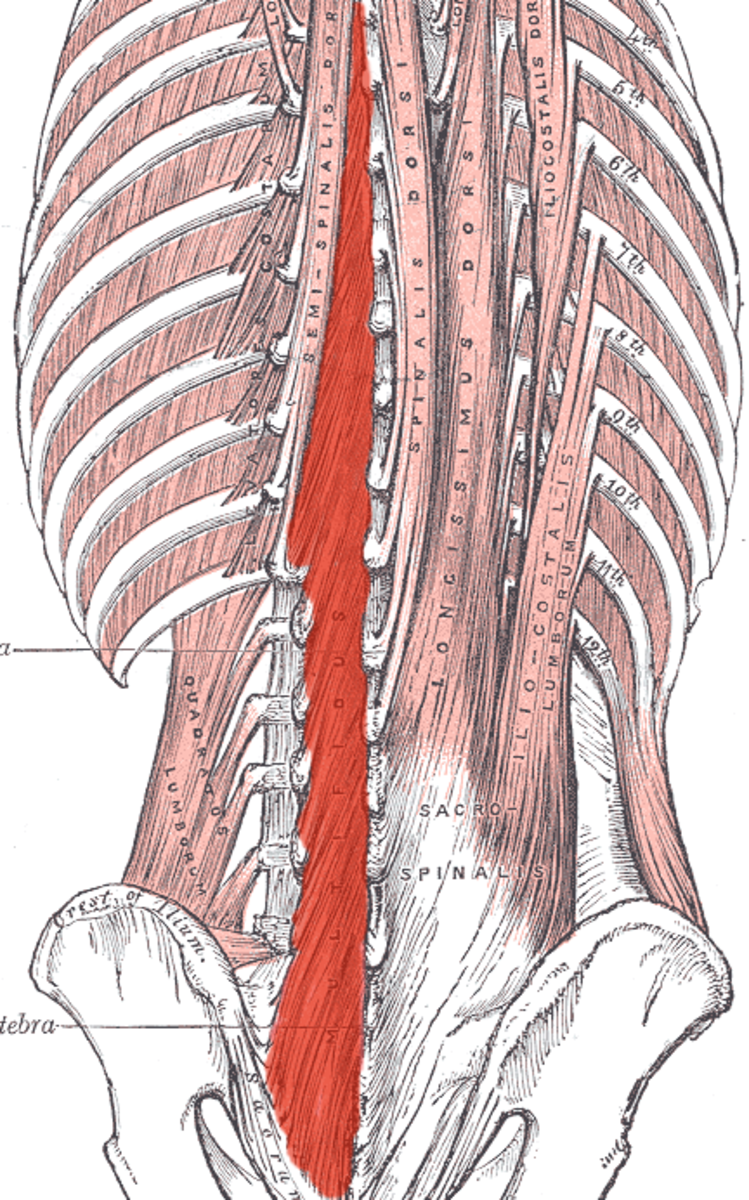
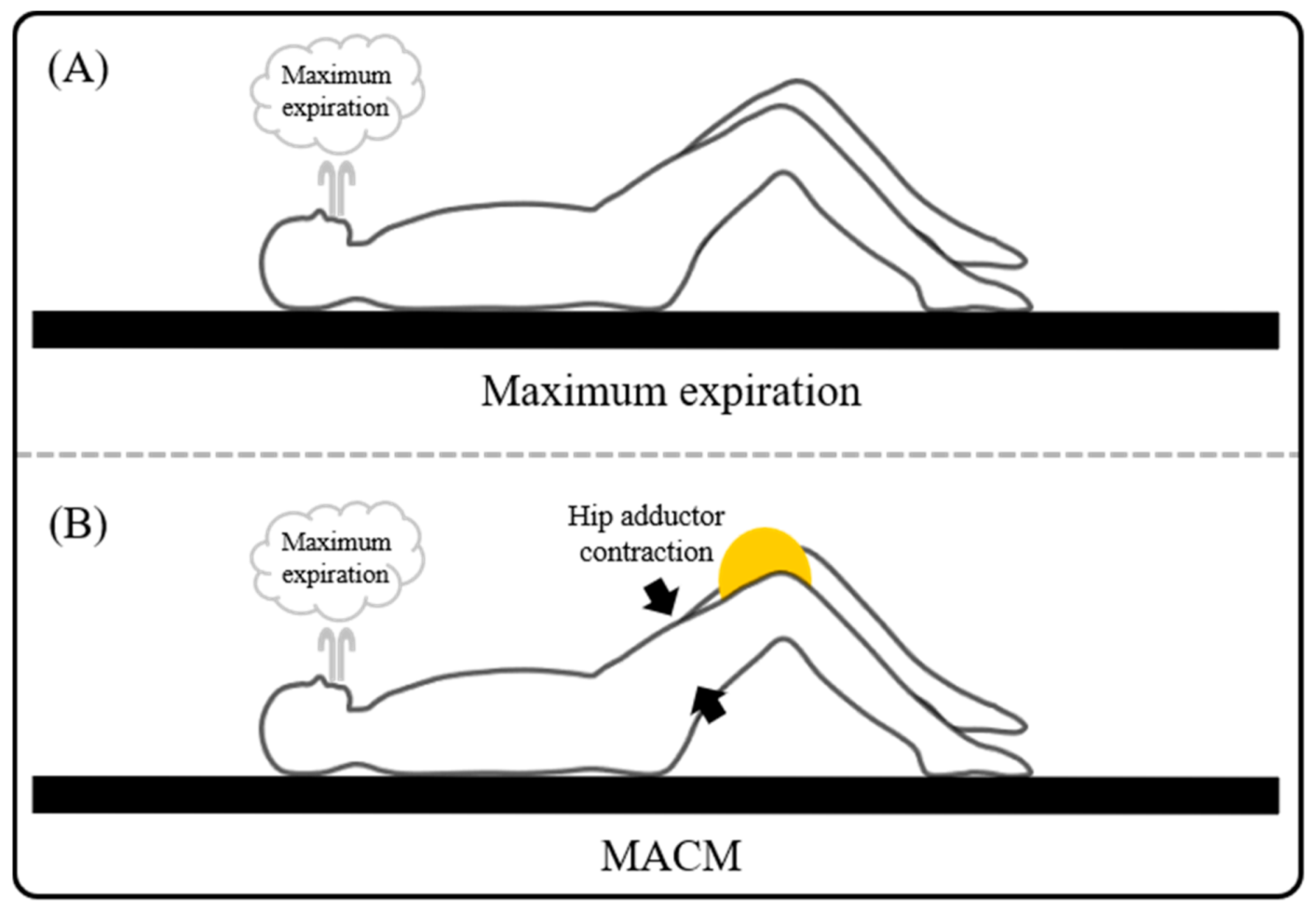
Background and objectives: The maximal abdominal contraction maneuver (MACM) was designed as an effective and efficient breathing exercise to increase the stability of the spinal joint. However, it has not been determined whether MACM is more effective and efficient than the maximal expiration method. Thus, the present study was undertaken to investigate whole abdominal muscle thickness changes after MACM. Materials and Methods: Thirty healthy subjects (17 males and 13 females) participated in this study. An experimental comparison between MACM and the maximal expiration task was conducted by measuring the change of abdominal muscle thickness such as the transverse abdominis (TrA), internal oblique (IO), external oblique (EO) and rectus abdominis (RA) using ultrasound images. Results: The results indicated that MACM resulted in significantly greater muscle thickness increases of the TrA and RA than the maximal expiration exercise (p < 0.05). Conclusion: MACM provided better exercise than the maximal expiration exercise in terms of increasing spine stability, at least from a co-contraction perspective.
Download 100,000+ Images From The History of Medicine, All Free Courtesy of The Wellcome Library
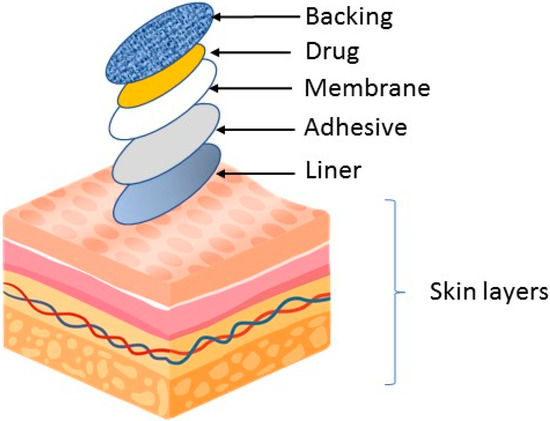
Medicina, Free Full-Text, Medical Patch
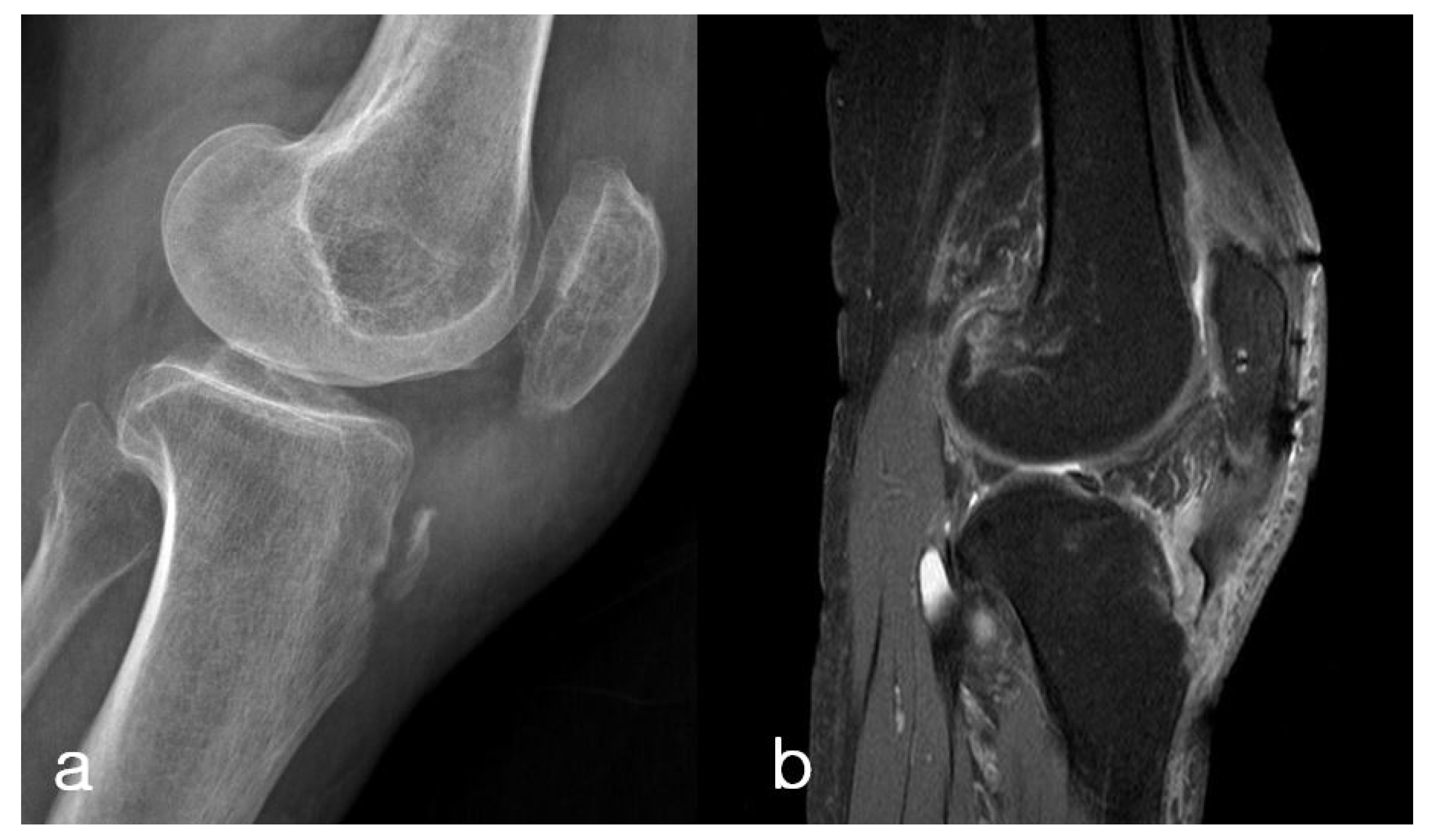
Sports Activity After Surgical Treatment of Intra-articular Tibial, bäumlein 108 led
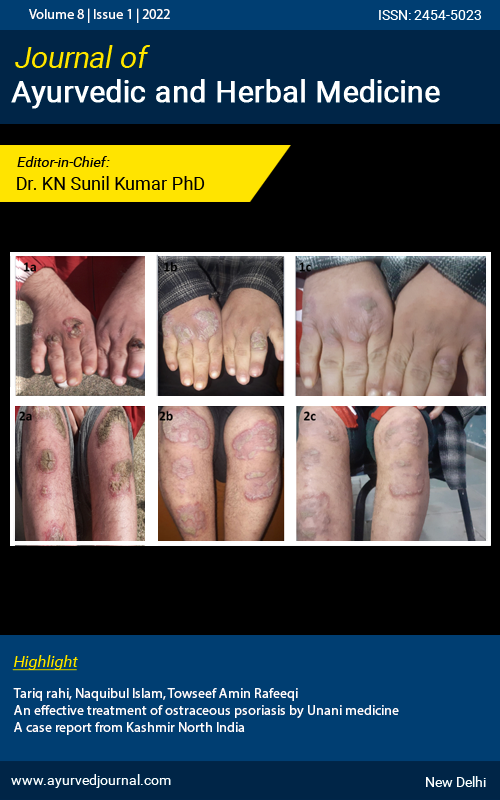
Ayurved Research : Journal of Ayurvedic and Herbal Medicine (JAHM)

Employer Sponsored Programs

IJERPH Free Full-Text Challenges In Preventive Practices
Bausch & Lomb Spectroscope - Science History Institute Digital, Spectroscope

Medicina, Free Full-Text, tibia rings
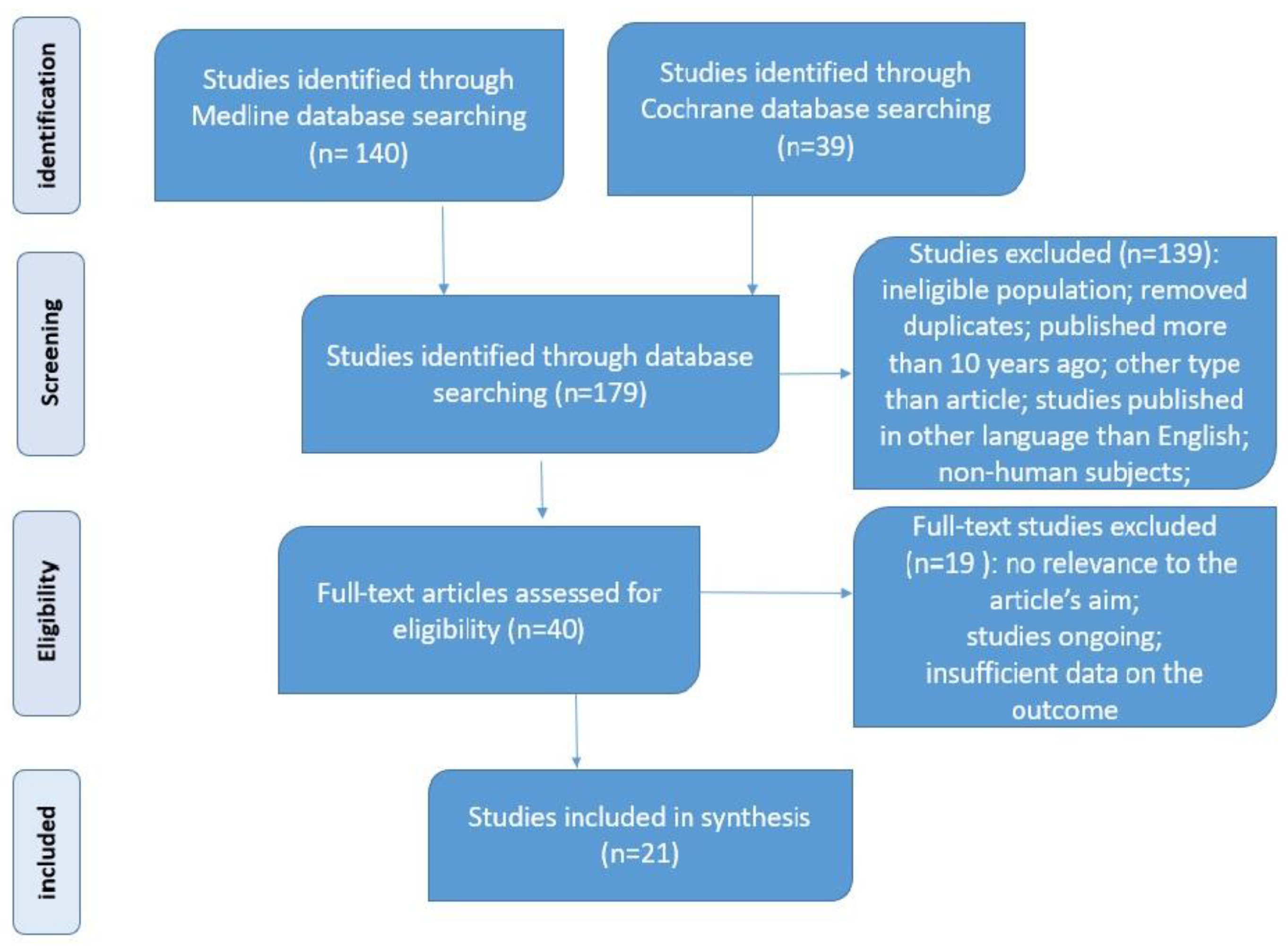
Medicina, Free Full-Text

Press Democrat Events - Author Appearance & Media Literacy Workshop (Free)

Medicina, Free Full-Text
Medicina, Free Full-Text